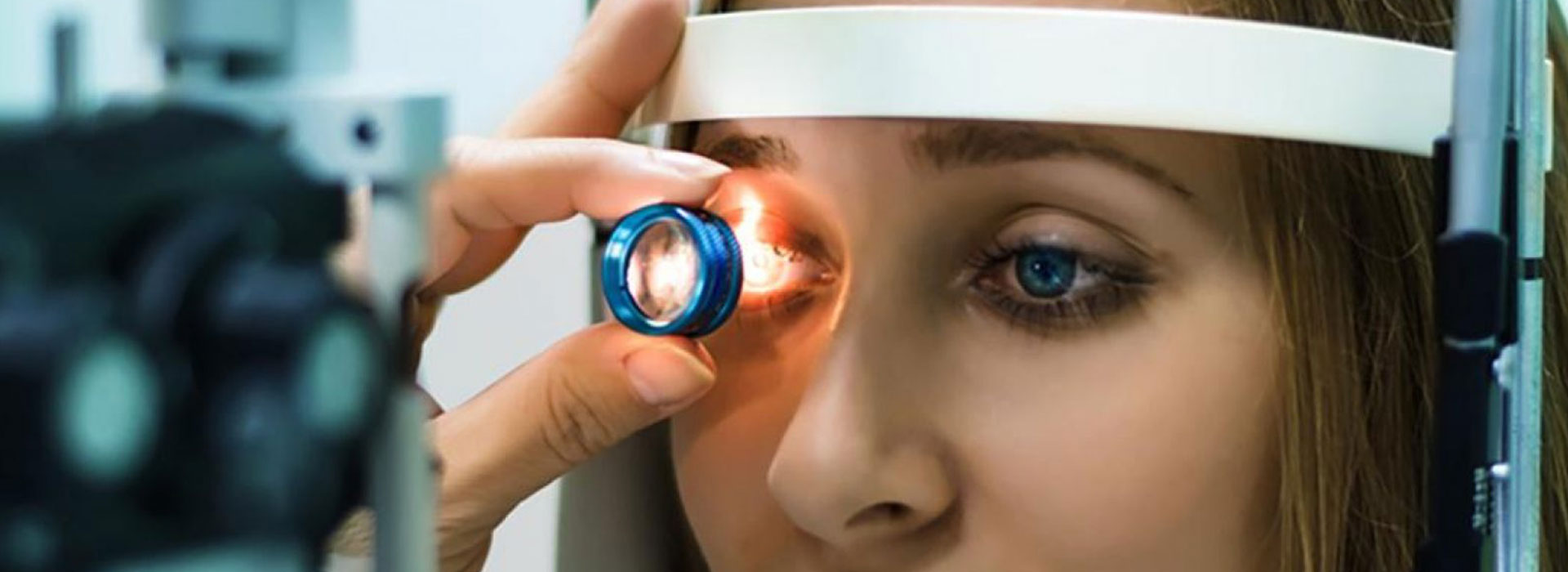
How to diagnose Glaucoma
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disease that affects the optic nerve head and the delicate nerve fibers.
It is characterized by:
- EYE PRESSURE INCREASE;
- OPTIC DISC ANATOMICAL ALTERATIONS;
- VISUAL FIELD ALTERATIONS.
It can be diagnosed with functional and morphometric tests, such as Visual Field Analysis, OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) and Tonometry.
OCT
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test that allows the ophthalmologist to take cross-section pictures of retina and see each of its distinctive layers.
Visual Field Test
It is a functional test that measures how sensitive the vision is in different parts of the visual field. It is done with the patient looking straight ahead at a small steady light.
Tonometry
It is a diagnostic test done with the tonometer. By measuring intraocular eye pressure, it helps doctor determine whether or not the patient may be at risk of glaucoma.
Types of glaucoma
- OPEN ANGLE GLAUCOMA;
- ACUTE ANGLE-CLOSURE GLAUCOMA;
- CONGENITAL GLAUCOMA (present from birth);
- SECONDARY GLAUCOMA (in the presence of other pathologies, such as diabetes, vein thrombosis, cancer or inflammations).
Symptoms
SUBSTANTIALLY ASYMPTOMATIC in the early stages. Symptoms like difficult peripheral vision or vision loss appear when the disease is usually quite advanced and not reversible with treatments.
ACUTE GLAUCOMA, however, is another matter altogether. Its symptoms come on suddenly and include severe headache, redness in the white part of the affected eye, nausea or vomiting and sudden loss of sight. It needs immediate pharmacological treatment (within the first few minutes after the crisis. In most cases however the vision will be permanently damaged in the affected eye. Despite the warning signals, like headache and eye redness, it is difficult to recognize it subjectively. It can almost be totally prevented when YAG LASER IRIDOTOMY recognizes an anatomic predisposition.
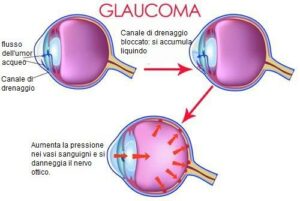
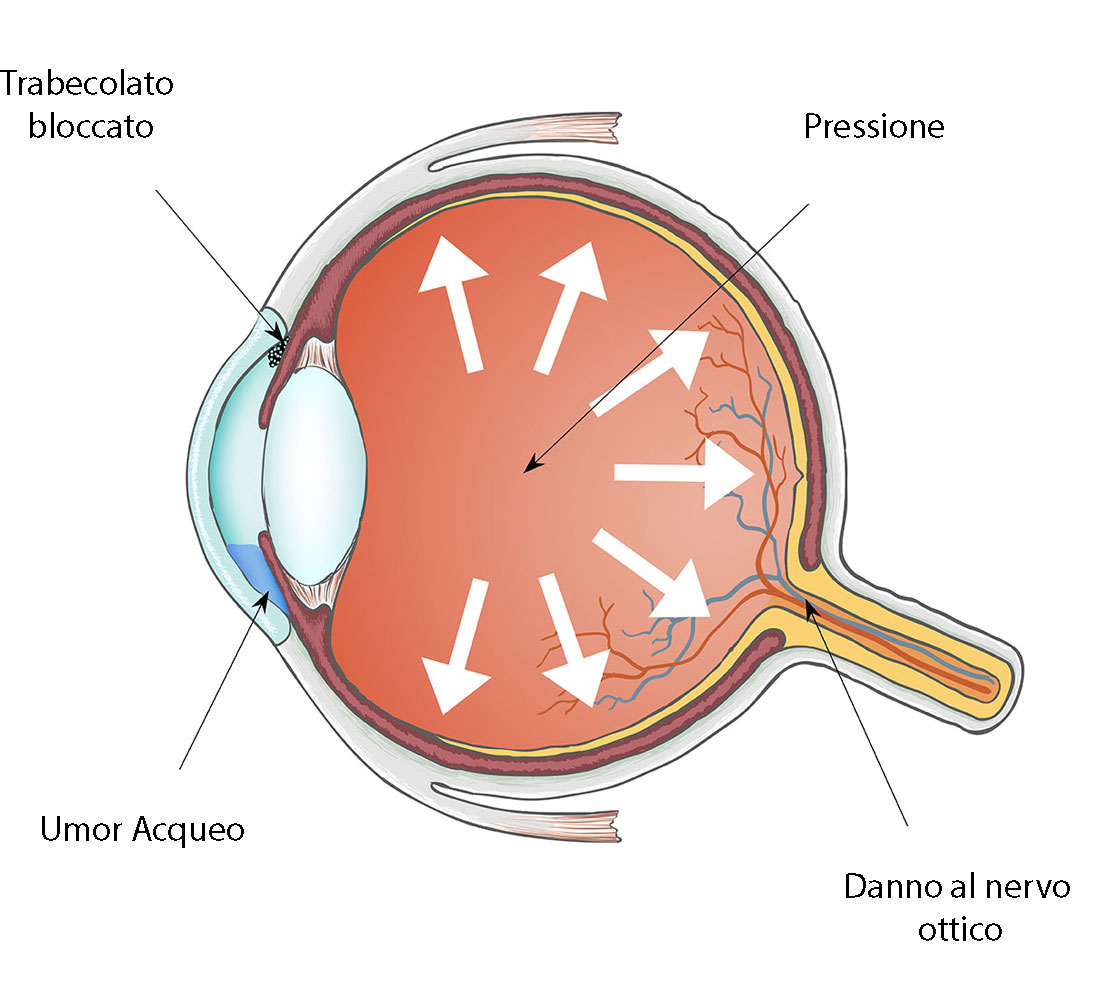
eye's pressure
Under normal conditions inside the eye there is a liquid (aqueous humor) which is continuously produced and reabsorbed. Therefore, the eye can be compared to a small tank with a tap and a drain always open: if the drain pipe is blocked, there will be an increase in pressure inside the tank (= increase in pressure in the eye). Similarly to what happens with a tire, if the pressure is too high in the long run, the eyeball will be damaged.
THE IMPORTANCE OF EARLY DIAGNOSIS
Over time, without any treatment, glaucoma can affect vision and eventually lead to blindness. If diagnosed and treated early, the disease progress can be arrested or reduced and the vision preserved. The aim of the therapy is to protect the central vision and the extention of the visual field as much as possible, in order to guarantee the highest quality of life to the patient.