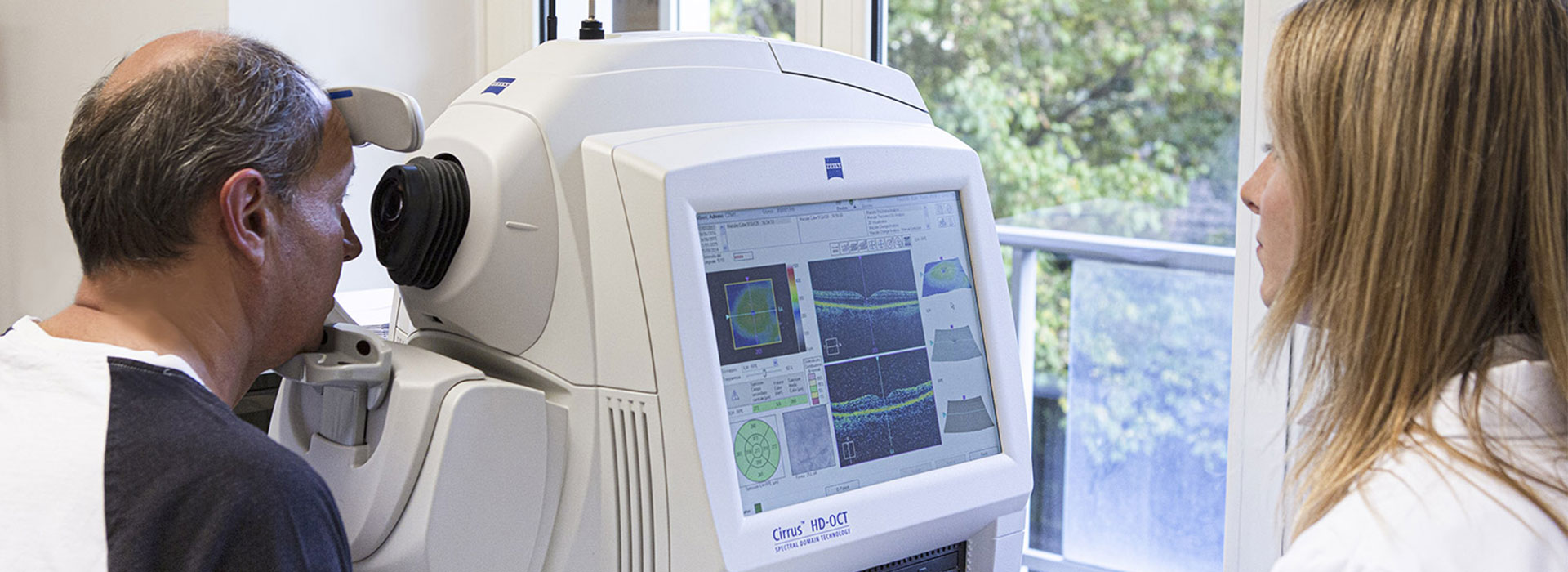
Retinal Diagnostic
What is the retina?
Retina is a layer of nervous tissue designated for the perception of the visual stimolous. It contains a lot of highly organized neuronal cells that are anatomically hidden, since they cover the back of the eyeball. Its correct functioning can be influenced by several pathologies: many of these may cause serious and disabling symptomatology, others may go unnoticed, especially in the early stages. Different types of diagnostic detection are useful to the ophthalmologist for their correct analysis, evaluation and follow-up. Optical Coherence Tomography, Autofluorescence Retinography and Computerized Visual Field Test are the most used.

Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)
LHON is a severe and progressive inherited mithocondrial disorder that can lead to an irreversible blindness.
What is it characterized by?
It usually starts with a sudden and painless visual field loss in one eye first and consequent appearance of central scotoma. The latter is a visual field defect strictly connected to a retinal sensitivity reduction. Affected patients can have an altered perception or even do not have it.
LHON presents commonly in young male (before 35 years of age) and its diagnosis has to be considered apart from age and gender, whereby clinic pathognomonic signs are clear.
We need to remember that Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy is a rare mithocondrial disease transmitted by maternal inheritance.
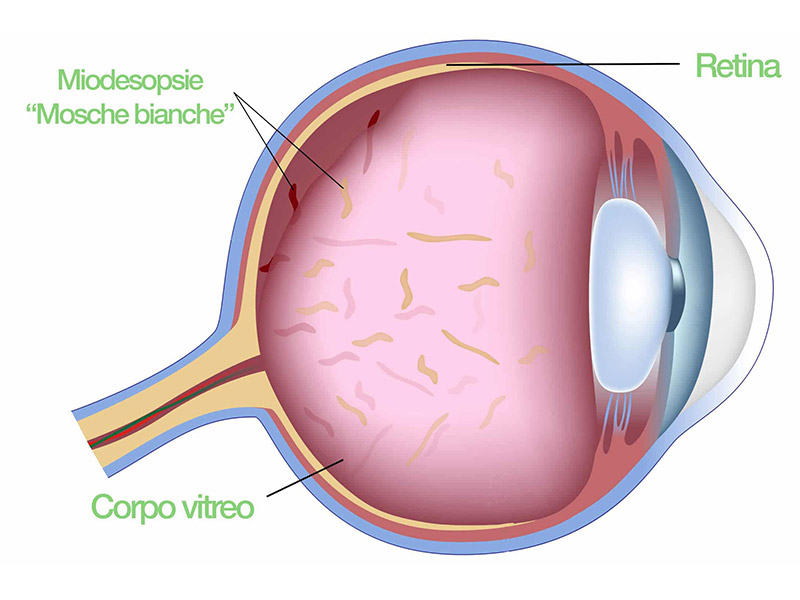
Myodesopsia
What are myodesopsias?
At the back of crystalline lens and next to the retina there is an acqueous gel-like fluid bag called vitreous humor. It is composed of collagen proteins that are well organized in order to guarantee the full transparency as light passes through. When this bag dries out, these proteins tend to clump and float within the eye. With the passage of light through the eye, they can cast real moving irregular shadows on the retina that the patient can perceive as “flies” or “cobwebs” moving on the background. Such condition, even though benign from a clinic perspective, can cause annoying difficulties to the patient’s vision.
Yag Laser Treatment
Until few years ago, the only possible treatment in order to solve the problem was the prolonged consumption of specific supplements for the eye. Nowadays, thanks to the MICROPULSED LASER, you can INSTANTLY remove it. Floaters treatment by Yag Laser is chosen when they are visible and distant from retina and crystalline lens. Yag Laser allows three basic methods: Vaporization, Delocalization and Reduction.
What are the techniques that can be used?
Vaporization hits directly fibrils contained in the mobile units, transforming them into gas. In case of posterior vitreous detachment, we have a hyaline ring that works very well during this treatment.
Delocalization is performed cutting the thin filaments at the top that let floater keep its position. In so doing, the floater falls low and does not interfere with the eyesight anymore.
The thinning method, instead, is chosen when floaters are multiple, fibrous and more difficult to vaporise. There can be a hundred of mobile units. Since such a high number of spots can not be highlighted, we tend to thin them out in order to not overheat vitreous.
In what consist the procedure?
The technique is simple, painless and lasts from 10 to 30 minutes. After some instillations of anaesthetic eye drops, the laser radiation is used to destroy mobile units. When the laser hits the target, a little flash of light and a cracking sound are noticed. In the meanwhile, the patient sees as if something is falling in the eye: tiny bubble of gas, created by the laser, that are moving towards the superior section. These bobble will go away within 24 hours.
Frequently it is necessary more than a treatment to get a complete resolution of the symptomatology.
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy is the latest treatment indicated for macular degeneration, i.e. a disease that hits the centre of the retina, the photosensitive membrane on which the images we see are impressed.
Nowadays, macular degeneration is the major cause of blindness in the world. Until few years ago, the only therapy was the laser treatment that, although limited damages derived from maculopathy, destroyed close tissues in an irreparable way, threatening the visual function.
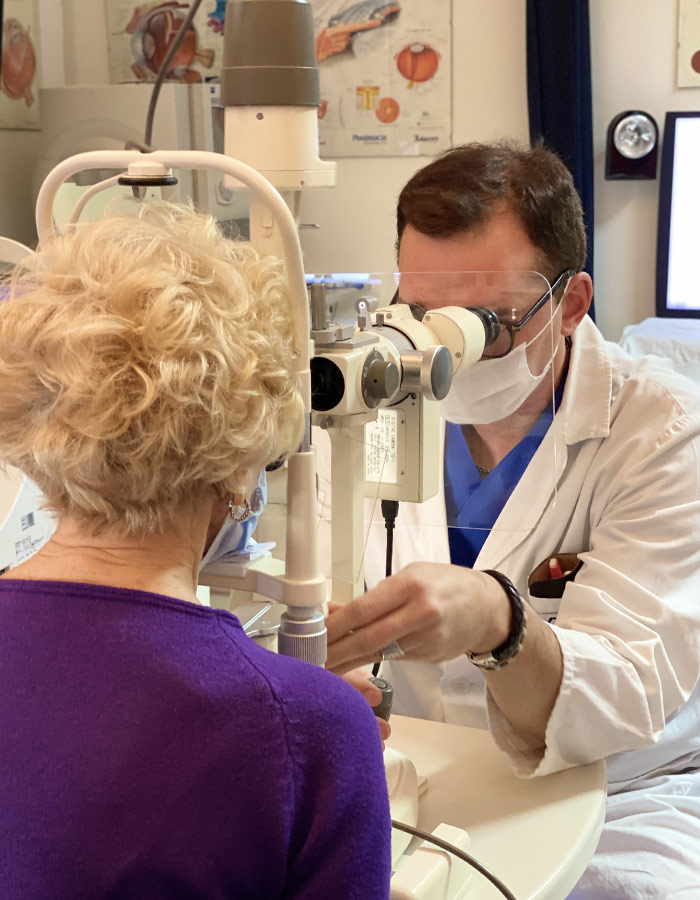
How can it be treated?
Photodynamic therapy is currently a new valid alternative. The treatment is divided into two phases. At the beginning, Verteporfin is injected into a vein and it gathers itself in the section affected by maculopathy; once it reaches the opportune concentration at the ocular level, the medicine destroys the abnormal blood vessels formed during the development of the disease, being excited after be exposed to the laser light with an appropriate wavelenght. In this way, the close tissues will not be damaged and the visual function protected.
Clinical studies, carried out so far, showed good results, opening a new orizon for the macular degeneration treatment. Anyway, beyond the demonstrated efficacy of the therapy, patients have at their disposal a therapeutic alternative capable of limiting damages caused by their disease, so far highly disabling.
Age-related Macular Degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration is an eye disease that hits the middle part of the retina (macula) and damages central vision. It usually affects 30% of the population over 75 years old.
It is a multifactorial pathology, since it can be linked to multiple risk factors:
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Smoking
- Sunlight
- High blood pressure
- Genetics
- Age (the progressively ageing of the retinal tissue)
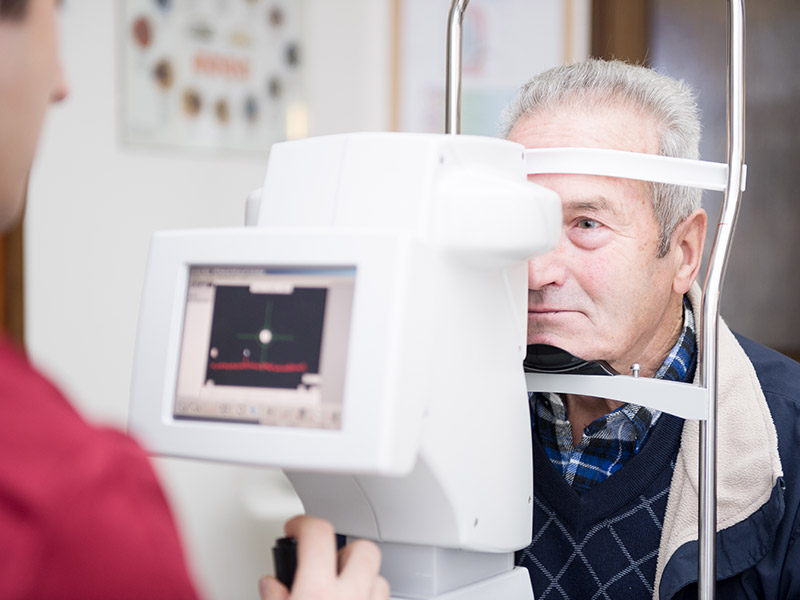
Symptoms
Symptoms are proportional to the extension and entity of the macular damage.
A key symptom in the assessment of a patient with age-related macular degeneration is the distorted vision, in which a grid of straight lines appears wavy (metamorphopsia). Progressively a black spot appears on the centre of the image and the patient is not able to distinguish faces and read anymore.
Diagnosis
It is important to have routine eye exams to identify early signs of macular degeneration, especially in the presence of risk factors. The AMSLER GRID can help to detect and monitor changes in vision at home. CX1 Fundus Camera for fluorescein angiography allows to do a fundus digitalised examination, recording the autofluorescence (typical property of the damaged retinal cells that consists in emitting fluorescence when the colorant is not injected systemically). In this non-invasive way, retinal damage can be detected before it arises. In the most advanced cases, Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green Angiography allows to identify subretinal neovessels.
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) offers a stratigraphy of the retina through which we can identify the presence of subretinal fluid and differentiate various forms of exudative maculopathy.
Treatment
In the ATROPHIC FORMS, according to an international orientation, it is recommended the use of vitamin supplements (antioxidant, zinc, selenium, and so on…). In the EXUDATIVE FORMS, in the presence of neovassels, treatments like intravitreal injections of antiangiogenic substances (AVASTIN, MACUGEN, LUCENTIS), ozonotherapy and selective laser treatments are the most indicated.
However, the treatment aims at slowing the disease down rather than curing it.